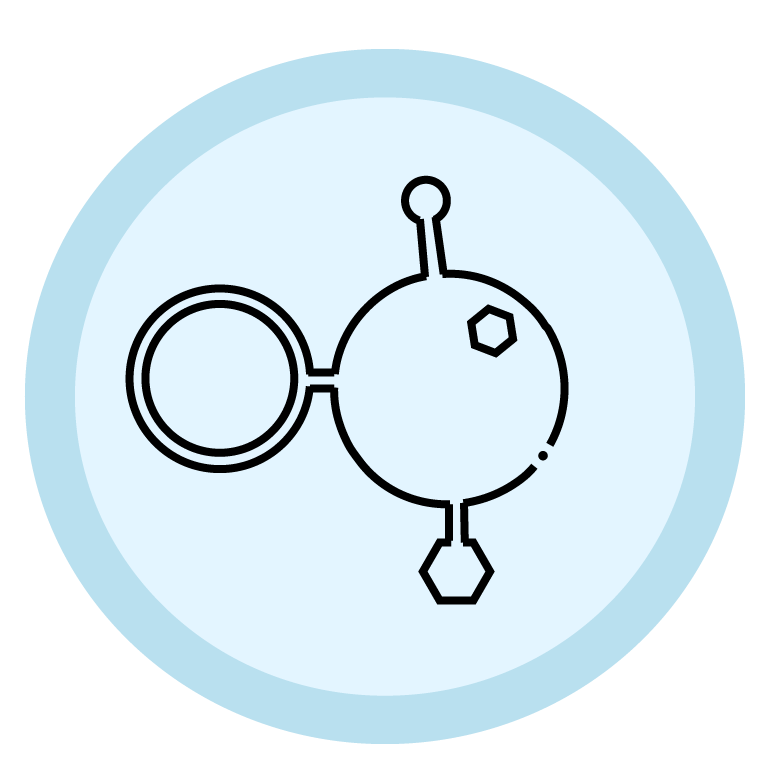
Choline is an essential nutrient that is required for the body to perform metabolic processes, and is found in certain types of food and available as a dietary supplement. It provides methyl groups, which are necessary for the formation of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin, two important phospholipids that are essential for the maintenance of cell membranes.
CHOLINE, WHAT IS IT FOR?

Utilization
HORMONES BALANCE
Choline is crucial for hormone production and regulation. It helps produce acetylcholine, needed to release hormones from the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, and phosphatidylcholine, vital for hormone receptor signaling.
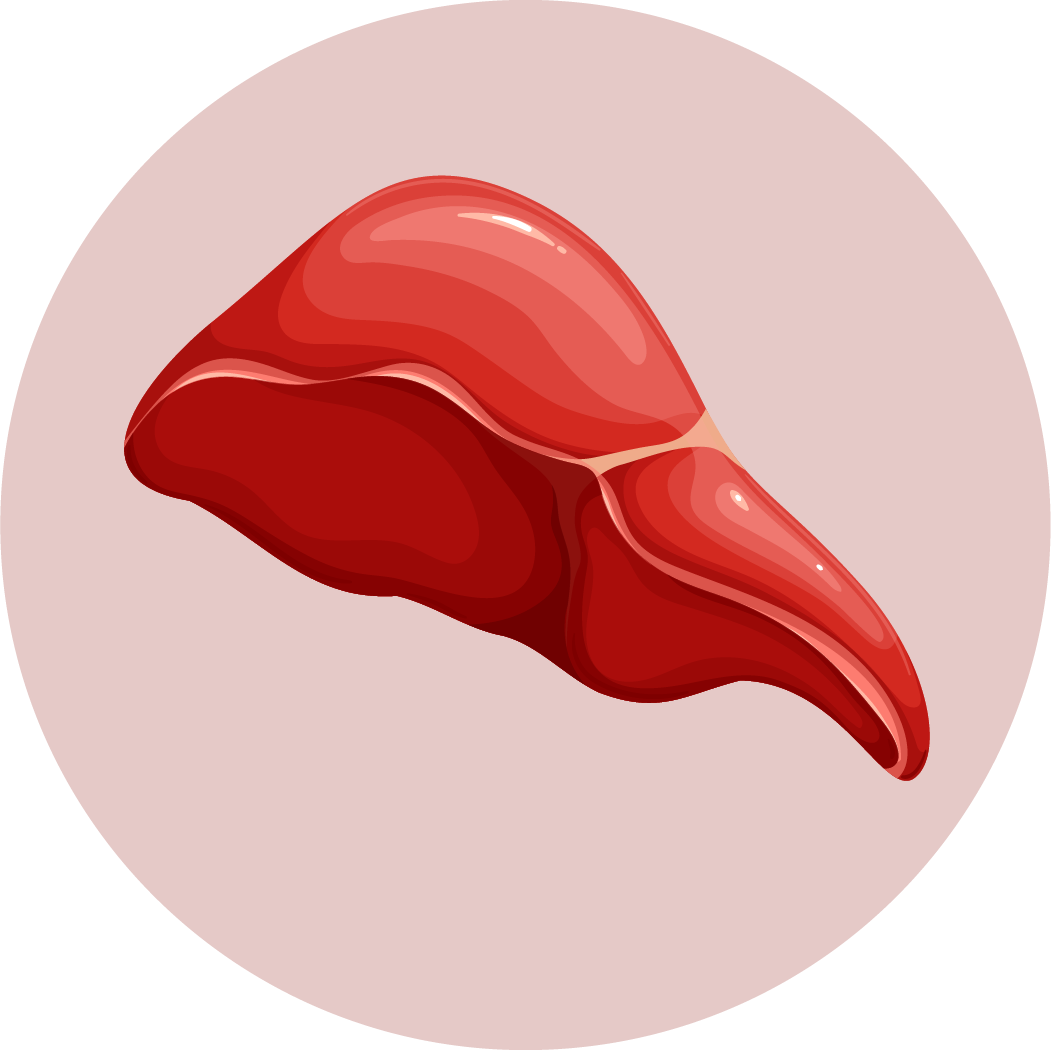
LIVER
Studies have shown that choline can help to protect the liver from damage caused by toxins and oxidative stress. It has also been shown to reduce the risk of fatty liver disease, a condition in which excess fat accumulates in the liver.
NERVE FUNCTION
Choline is an essential nutrient that is required for the synthesis of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is involved in numerous functions in the body, including muscle movement, memory, and mood regulation

METABOLISM
Choline serves as a methyl donor, which is important for the methylation process, a critical step in the metabolism of several compounds in the body.

DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Choline helps to protect the stomach lining by strengthening the mucosal layer and reducing the production of stomach acid.
COGNITIVE FUNCTION
Studies have shown that choline can improve cognitive function, particularly in tasks related to memory and information processing. It has also been shown to have a protective effect on the brain as we age, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Deficiency

BLOOD PRESSURE
Recent studies suggest that the deficiency is linked to an increased risk of high blood pressure. Researchers have found that choline plays a vital role in regulating the levels of homocysteine, an amino acid that can cause inflammation and arterial damage, leading to hypertension.
BRAIN FUNCTION
Mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder have been linked to low levels of choline It’s necessary to make sure you are consuming adequate choline since the body cannot produce enough of it by itself.

LIVER
Unfortunately, some studies have suggested that having too little choline in your diet can lead to liver damage. Conversely, too much can also cause damage to the liver. This can be particularly problematic for people with pre-existing liver issues. As well as those who are consuming large amounts of supplements that contain choline.
GROWTH
One study found that children with a choline deficiency were significantly shorter than those with adequate choline levels. Additionally, animal studies have shown that deficiency during pregnancy can impact the growth and development of offspring.
KIDNEYS
While choline is generally safe to consume, studies have shown that high choline intake may be associated with an increased risk of kidney disease. As well as a greater mortality rates among people with kidney impairment. Vitamin B5 LIVER Unfortunately, some studies have suggested that having too little choline in your diet can lead to liver damage. Conversely, too much can also cause damage to the liver. This can be particularly problematic for people with pre-existing liver issues. As well as those who are consuming large amounts of supplements that contain